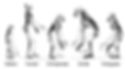
"A monkey that jumped on the trees
Has worn a man's attire"
These are from the lyrics of an old film song in Malayalam. The poet is probably mocking the lack of consistency and moral convictions of humans. There is a synonym for monkey in Malayalam, "Vaanaran" literally meaning 'man with a tail'. But is a monkey actually a man with a tail? Science will never say so. What is the difference between a monkey and an ape?
A monkey has a tail - an ape doesn't have a tail.
An ape often is a biped - a monkey naturally walks on fours.
An ape has long and strong arms - whereas a monkey's legs are longer than it's arms.
The monkey's movement is to jump on trees - when moving on a tree the ape's way of moving is brachiation with its arms. Apes are basically animals that came down from the trees.
Apes have broad chest and larger shoulders, whereas monkeys have thin chest and small shoulders.
Scientifically, apes have a lot more developed brains than the monkeys.
Even according to biology, apes are only distantly related to humans. When we say hominids, which include apes, humans, and their ancestors, humans and their ancestors aside from the apes are called hominins. Including monkeys collectively we call primates.
Apes include orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees, gibbons, macaques, and bonobos. However, only chimpanzees and humans are considered to have evolved from the same ancestor. (Something like the relatedness between elephants and shrews.) Which means, although chimps are the closest branch to humans, all other apes were branched out and separated from us very very long ago.
Again, that means, science does not consider any species of apes or monkeys living today to be the ancestors of humans.
The main turning points behind our becoming human are said to be the upright walking, the development of the brain, and the ability to bring the tips of the thumb and index finger together.
Of these, if we take the brain alone, it was thought to be the ratio of brain size to body mass that was the decisive factor. However, the scientists now say that it is not only the size of the brain, but also the part of the brain where a lot of nerves are concentrated to. Besides, how much energy is provided to the brain is also very important. The human brain is 1100-1700 cubic cm in size. (On average, 2.72 Ibs), accounts for 2% of the body. 20% of our energy is spent on this 2% section of our body.
The African elephant has a brain that is 1.33 Ibs larger than that of humans. The brain of chimpanzees is only one-third the size of a human'. The brains of gorillas and orangutans are 0.83 Ibs. While they have 9.1 billion neurons connected in their cortex - the area of thought and intelligence, the African elephant has only 5.59 billion neurons connected. In humans, this is 16.3 billion.
If we ask how this large brain size and such a high concentration of neurons occurred in human evolution, they say that humans got their brains enlarged by reducing their gut. Humans put more energy into the brain by reducing the amount of energy we supply to the muscles of the body! In other words, no matter how muscular a man is, an ape of the same size will be physically stronger than him.
It is also said that when humans learned to make fire and cook food, may have led to the decrease in the gut size and an increase in head size!
How much more do we still have to learn about ourselves!